JPCERT-AT-2022-0006
JPCERT/CC
2022-02-10(Initial)
2022-05-27(Update)
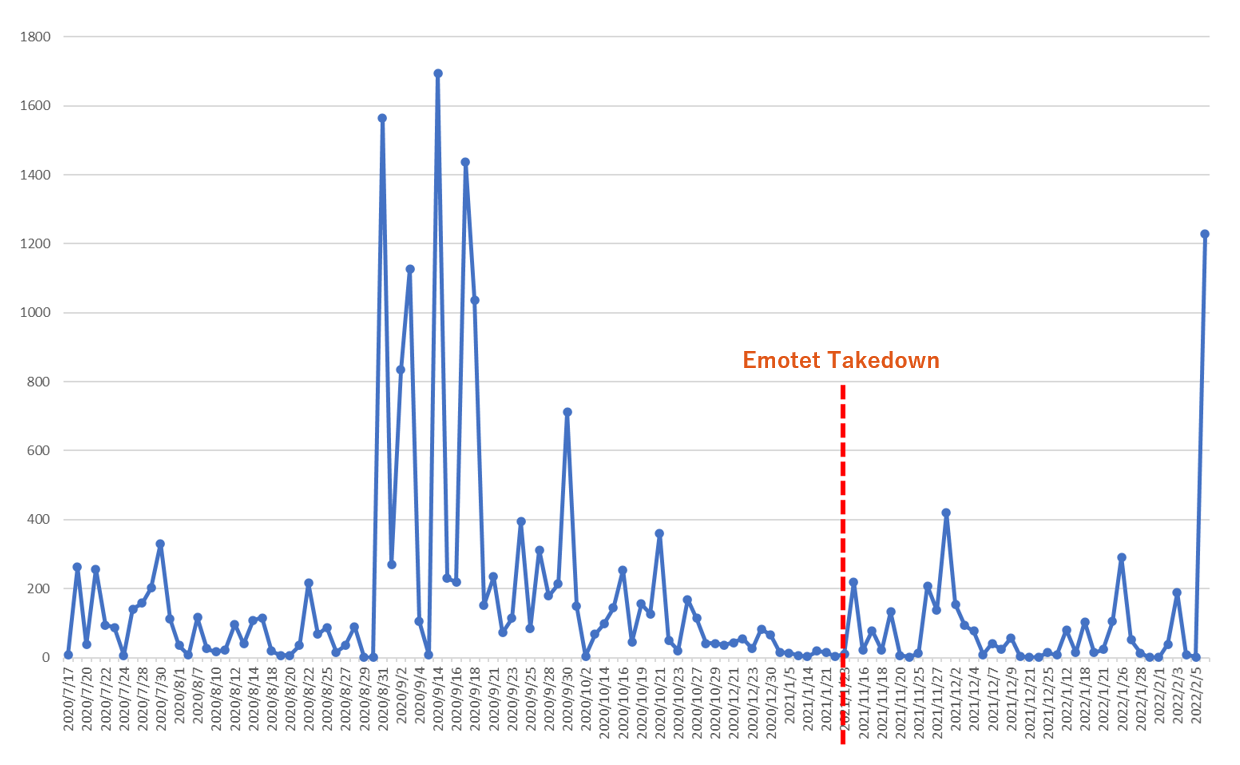
The number of .jp email addresses that may be infected with Emotet and abused in malspam activities has significantly increased. Since the Emotet activity is almost as severe as 2020 when Emotet infections were very active, JPCERT/CC recommends checking whether appropriate measures are taken against Emotet.
[Figure1: Number of .jp email addresses that may be infected with Emotet and abused for malspam activities (Data provided by trusted third party)]
In addition to these methods, JPCERT/CC has also observed cases where malicious Excel and Word files are downloaded by clicking a link in the body of an email, or Emotet infection through a link that is pretending to be for installing an application on Windows.
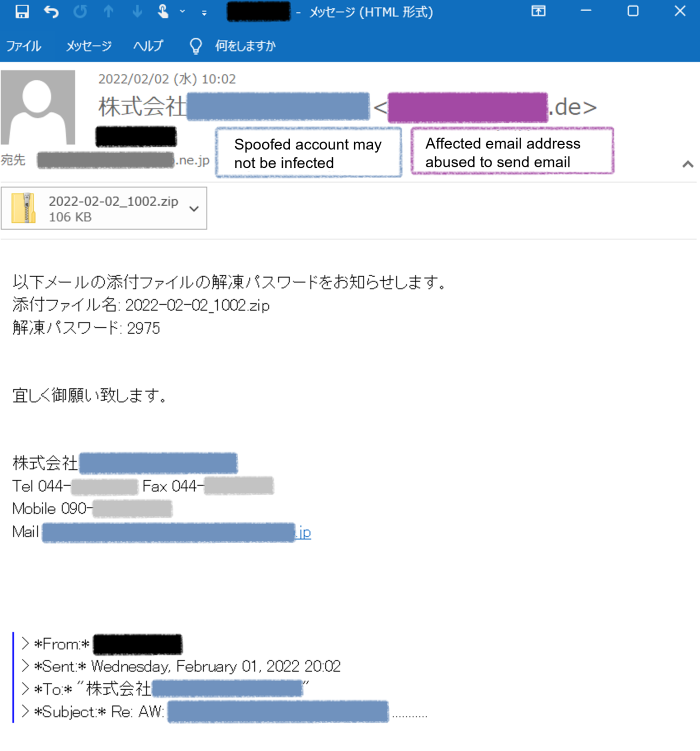
The body of the email and the attached file contain the content that prompts users to open the attached file and enable content or macro.The following is a sample email confirmed by JPCERT/CC.
[Figure2: Emotet email sample]
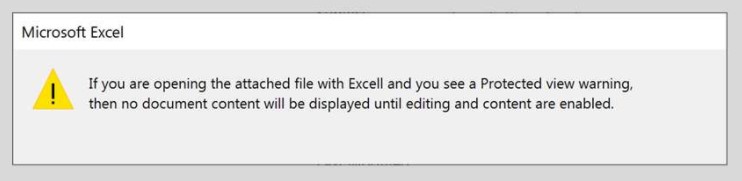
[Figure3: Example message that prompts users to execute a macro that is displayed upon opening the attached file]
It is recommended not to open the attached file or link unless it can be trusted although the email looks to be coming from a business partner or acquaintance.
How to Respond to Emotet Infection (FAQ)
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/ja/2019/12/emotetfaq.html (Japanese)
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/en/2019/12/emotetfaq.html (English)
EmoCheck: Emotet detection tool for Windows OS
https://github.com/JPCERTCC/EmoCheck/releases
Please use the latest version of EmoCheck.
On May 27, 2022, JPCERT/CC released v2.3.2 of EmoCheck.
Check the following file for more information.
https://github.com/JPCERTCC/EmoCheck/blob/master/README.md
JPCERT/CC
How to check Emotet infection and respond (Released on March 7, 2022) (JAPANESE)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nqxikr1x2ag
JPCERT/CC Analysis Center (JAPANESE)
https://twitter.com/jpcert_ac/status/1491259846616023044
Information-technology Promotion Agency, Japan (IP)
Surge in the numbers of Emotet infection activities (Updated on Feb 9, 2022) (JAPANESE)
https://www.ipa.go.jp/security/announce/20191202.html#L18
JPCERT/CC Alert
Alert Regarding Emotet Malware Infection
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/english/at/2019/at190044.html
JPCERT/CC
Emotet Malware spreading in Japan (Released on March 7, 2022) (JAPANESE)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wvu9sWiB2_U
2022-02-15 Updated "II. Observed Emotet features and trends" and "III. Response"
2022-02-17 Updated "II. Observed Emotet features and trends" and "III. Response"
2022-03-03 Updated "I. Overview" and "II. Observed Emotet features and trends"
2022-03-07 Updated "III. Response"
2022-03-08 Updated "III. Response" and "IV. References"
2022-03-14 Updated "IV. References"
2022-04-22 Updated "III. Response"
2022-04-26 Updated "II. Observed Emotet features and trends"
2022-05-20 Updated "III. Response"
2022-05-24 Updated "III. Response"
2022-05-27 Updated "III. Response"
JPCERT Coordination Center (Early Warning Group)
For questions or reports on this alert
MAIL: ew-info@jpcert.or.jp
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/english/
For request of support for incident response
JPCERT Coordination Center (Incident Response Group)
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/form/ (JAPANESE)
JPCERT/CC
2022-02-10(Initial)
2022-05-27(Update)
I. Overview
JPCERT/CC has received many reports regarding the infection of the malware Emotet, which has been confirmed to resume its activities since the late November 2021. The number of reports has increased in particular since the first week of February 2022.The number of .jp email addresses that may be infected with Emotet and abused in malspam activities has significantly increased. Since the Emotet activity is almost as severe as 2020 when Emotet infections were very active, JPCERT/CC recommends checking whether appropriate measures are taken against Emotet.
[Figure1: Number of .jp email addresses that may be infected with Emotet and abused for malspam activities (Data provided by trusted third party)]
II. Observed Emotet features and trends
Emotet that has been observed since the late November 2021 is mainly distributed through emails as an Excel or Word file with macros (or as a password protected Zip file containing such file). Enabling the macro after opening the file leads to the infection of Emotet.In addition to these methods, JPCERT/CC has also observed cases where malicious Excel and Word files are downloaded by clicking a link in the body of an email, or Emotet infection through a link that is pretending to be for installing an application on Windows.
The body of the email and the attached file contain the content that prompts users to open the attached file and enable content or macro.The following is a sample email confirmed by JPCERT/CC.
[Figure2: Emotet email sample]
[Figure3: Example message that prompts users to execute a macro that is displayed upon opening the attached file]
Update: April 26, 2022 Update
From around April 25, 2022, emails with a shortcut file (LNK file) or a password-protected Zip file containing the shortcut file that lead to the Emotet infection have been observed. Executing the file drops and executes a script file that downloads and installs Emotet.
The new method may have been introduced to infect without requiring email recipients to enable macros or content on Microsoft Word or Excel.
The new method may have been introduced to infect without requiring email recipients to enable macros or content on Microsoft Word or Excel.
It is recommended not to open the attached file or link unless it can be trusted although the email looks to be coming from a business partner or acquaintance.
Update: February 15, 2022 Update
After this alert was released, we have received inquiries about Emotet infection from multiple organizations. Cases where an email is sent due to an Emotet infection are divided into multiple patterns that involve the infected accounts and their stakeholders.
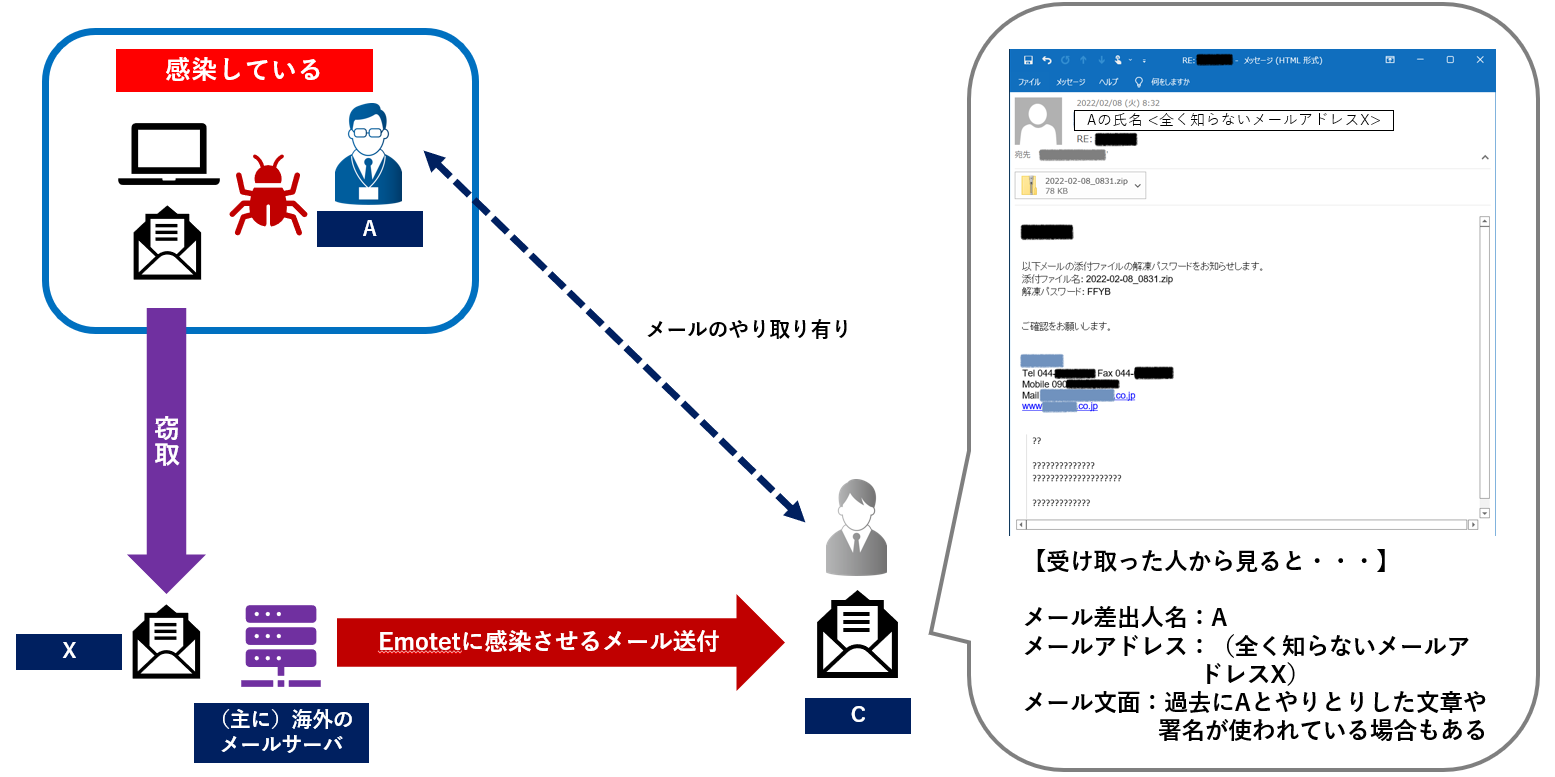
1) A case where your organization is infected with Emotet and a spoofed email is delivered.
When infected with Emotet, information such as email information stored in the infected device and the name of the person in charge registered in the address book is stolen. The stolen information can be abused in spoofed emails that lead to Emotet infections.
[Fig. 4: Case where your organization is infected with Emotet and spoofed emails are delivered (Japanese)]
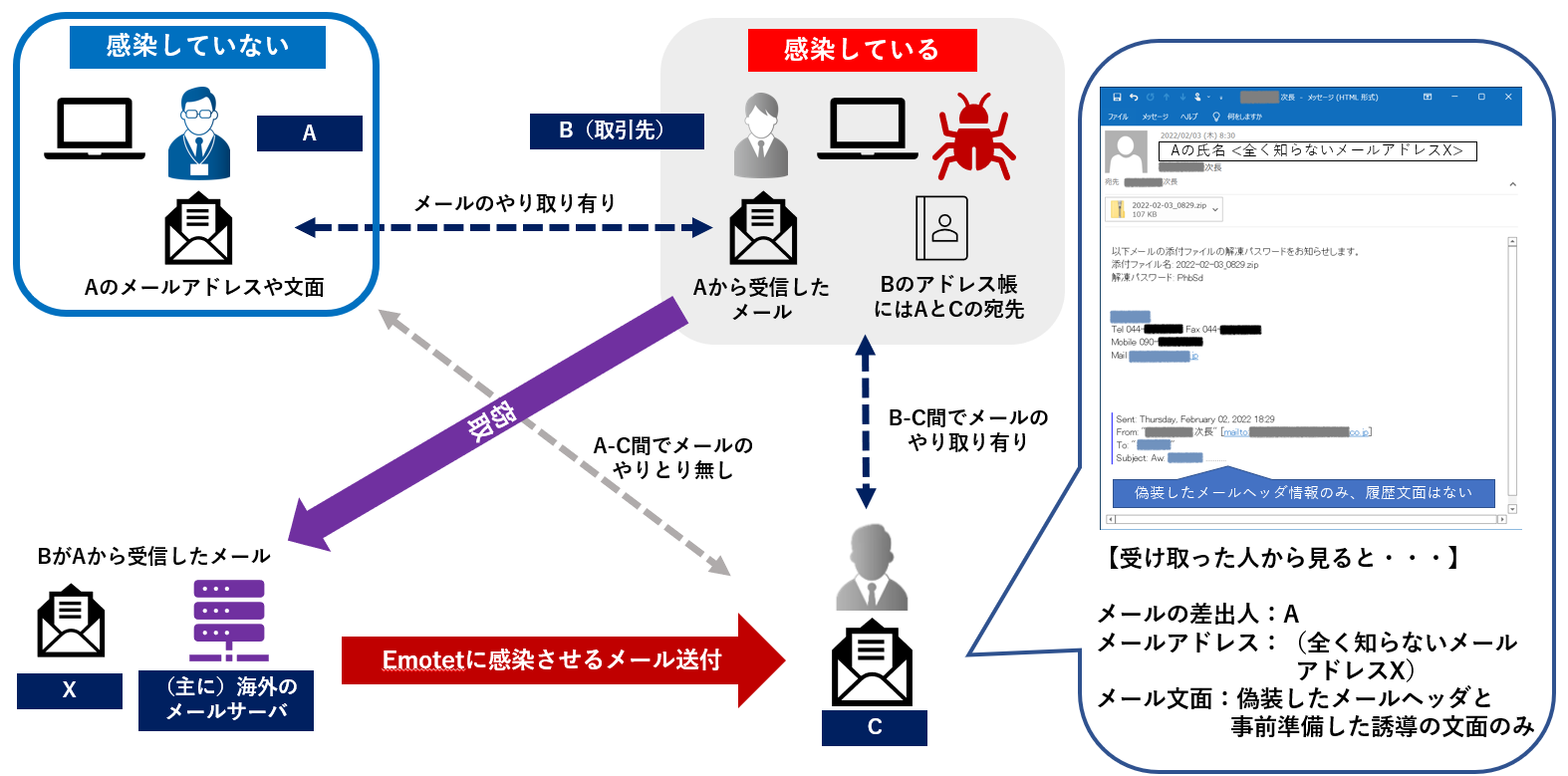
2) A case where a business partner is infected with Emotet and a spoofed email is delivered.
Just because an email impersonating an employee of your organization is observed, it does not always mean that the employee's device is infected with Emotet. There is a possibility that the device of a business partner with whom the employee has exchanged emails in the past has been infected with Emotet, and the information of the employee that was included in the stolen information from the business partner has been abused.
[Figure 5: A case where a business partner is infected with Emotet and a spoofed email is delivered (Japanese)]
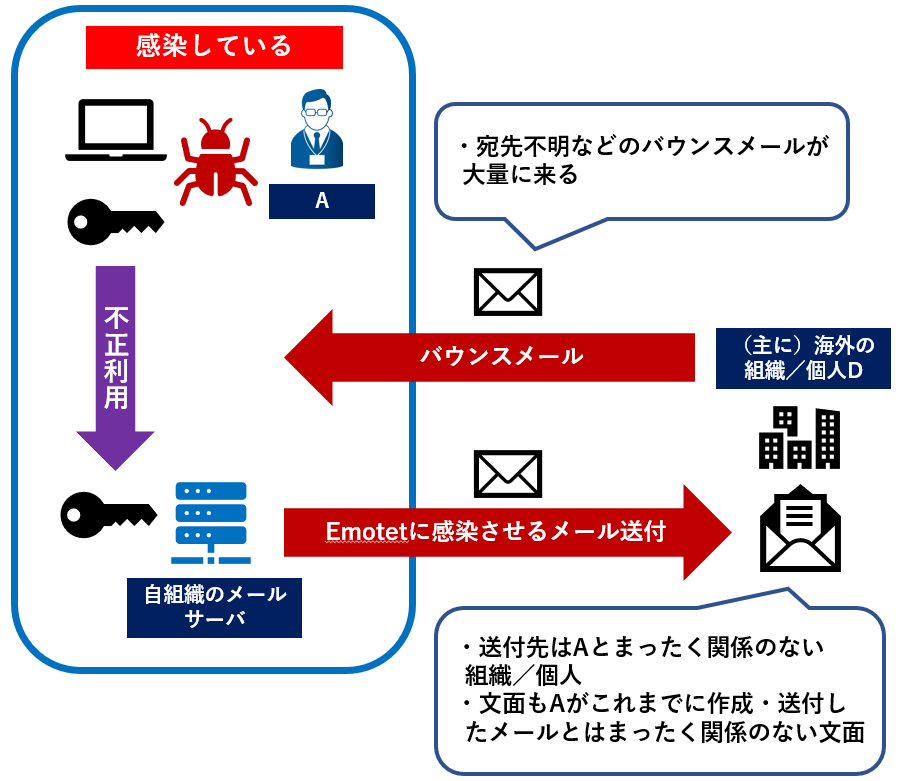
Also, since there are cases where Emotet emails have been sent from Japanese mail servers, JPCERT/CC recommends checking if the infrastructure such as the mail server managed by your organization is not being abused. If abused, the servers may have received a large number of bounce emails, for example because Emotet emails have not been delivered to some of the destination addresses.
[Figure 6: Case of receiving a large amount of bounce emails due to Emotet infection (Japanese)]
If an email impersonating an employee of your organization is observed, it is recommended to confirm and check the situation how the email was sent among the parties concerned, and take appropriate actions by referring to the information such as the following FAQ described later.
1) A case where your organization is infected with Emotet and a spoofed email is delivered.
When infected with Emotet, information such as email information stored in the infected device and the name of the person in charge registered in the address book is stolen. The stolen information can be abused in spoofed emails that lead to Emotet infections.
[Fig. 4: Case where your organization is infected with Emotet and spoofed emails are delivered (Japanese)]
2) A case where a business partner is infected with Emotet and a spoofed email is delivered.
Just because an email impersonating an employee of your organization is observed, it does not always mean that the employee's device is infected with Emotet. There is a possibility that the device of a business partner with whom the employee has exchanged emails in the past has been infected with Emotet, and the information of the employee that was included in the stolen information from the business partner has been abused.
[Figure 5: A case where a business partner is infected with Emotet and a spoofed email is delivered (Japanese)]
Also, since there are cases where Emotet emails have been sent from Japanese mail servers, JPCERT/CC recommends checking if the infrastructure such as the mail server managed by your organization is not being abused. If abused, the servers may have received a large number of bounce emails, for example because Emotet emails have not been delivered to some of the destination addresses.
[Figure 6: Case of receiving a large amount of bounce emails due to Emotet infection (Japanese)]
If an email impersonating an employee of your organization is observed, it is recommended to confirm and check the situation how the email was sent among the parties concerned, and take appropriate actions by referring to the information such as the following FAQ described later.
III. Response
Please refer to the following blog and tool for the response to Emotet infection.How to Respond to Emotet Infection (FAQ)
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/ja/2019/12/emotetfaq.html (Japanese)
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/en/2019/12/emotetfaq.html (English)
EmoCheck: Emotet detection tool for Windows OS
https://github.com/JPCERTCC/EmoCheck/releases
Please use the latest version of EmoCheck.
On May 27, 2022, JPCERT/CC released v2.3.2 of EmoCheck.
Check the following file for more information.
https://github.com/JPCERTCC/EmoCheck/blob/master/README.md
JPCERT/CC
How to check Emotet infection and respond (Released on March 7, 2022) (JAPANESE)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nqxikr1x2ag
Update: February 15, 2022 Update
We advise using EmoCheck with the Windows user account suspected to be infected with Emotet. EmoCheck may not be able to properly detect Emotet if executed by another user account,
IV. References
JPCERT/CC Analysis Center (JAPANESE)
https://twitter.com/jpcert_ac/status/1491259846616023044
Information-technology Promotion Agency, Japan (IP)
Surge in the numbers of Emotet infection activities (Updated on Feb 9, 2022) (JAPANESE)
https://www.ipa.go.jp/security/announce/20191202.html#L18
JPCERT/CC Alert
Alert Regarding Emotet Malware Infection
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/english/at/2019/at190044.html
JPCERT/CC
Emotet Malware spreading in Japan (Released on March 7, 2022) (JAPANESE)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wvu9sWiB2_U
Revision History
2022-02-10 First edition2022-02-15 Updated "II. Observed Emotet features and trends" and "III. Response"
2022-02-17 Updated "II. Observed Emotet features and trends" and "III. Response"
2022-03-03 Updated "I. Overview" and "II. Observed Emotet features and trends"
2022-03-07 Updated "III. Response"
2022-03-08 Updated "III. Response" and "IV. References"
2022-03-14 Updated "IV. References"
2022-04-22 Updated "III. Response"
2022-04-26 Updated "II. Observed Emotet features and trends"
2022-05-20 Updated "III. Response"
2022-05-24 Updated "III. Response"
2022-05-27 Updated "III. Response"
JPCERT Coordination Center (Early Warning Group)
For questions or reports on this alert
MAIL: ew-info@jpcert.or.jp
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/english/
For request of support for incident response
JPCERT Coordination Center (Incident Response Group)
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/form/ (JAPANESE)