JPCERT-AT-2019-0044
JPCERT/CC
2019-11-27(Initial)
2019-12-10(Update)
Following this situation, in order to prevent further impact caused by Emotet malware, JPCERT/CC decided to publish this alert to share the primary infection vector of Emotet and its impact, as well as some tips on how to detect and defend against Emotet infection, and how to respond once the infection is confirmed.
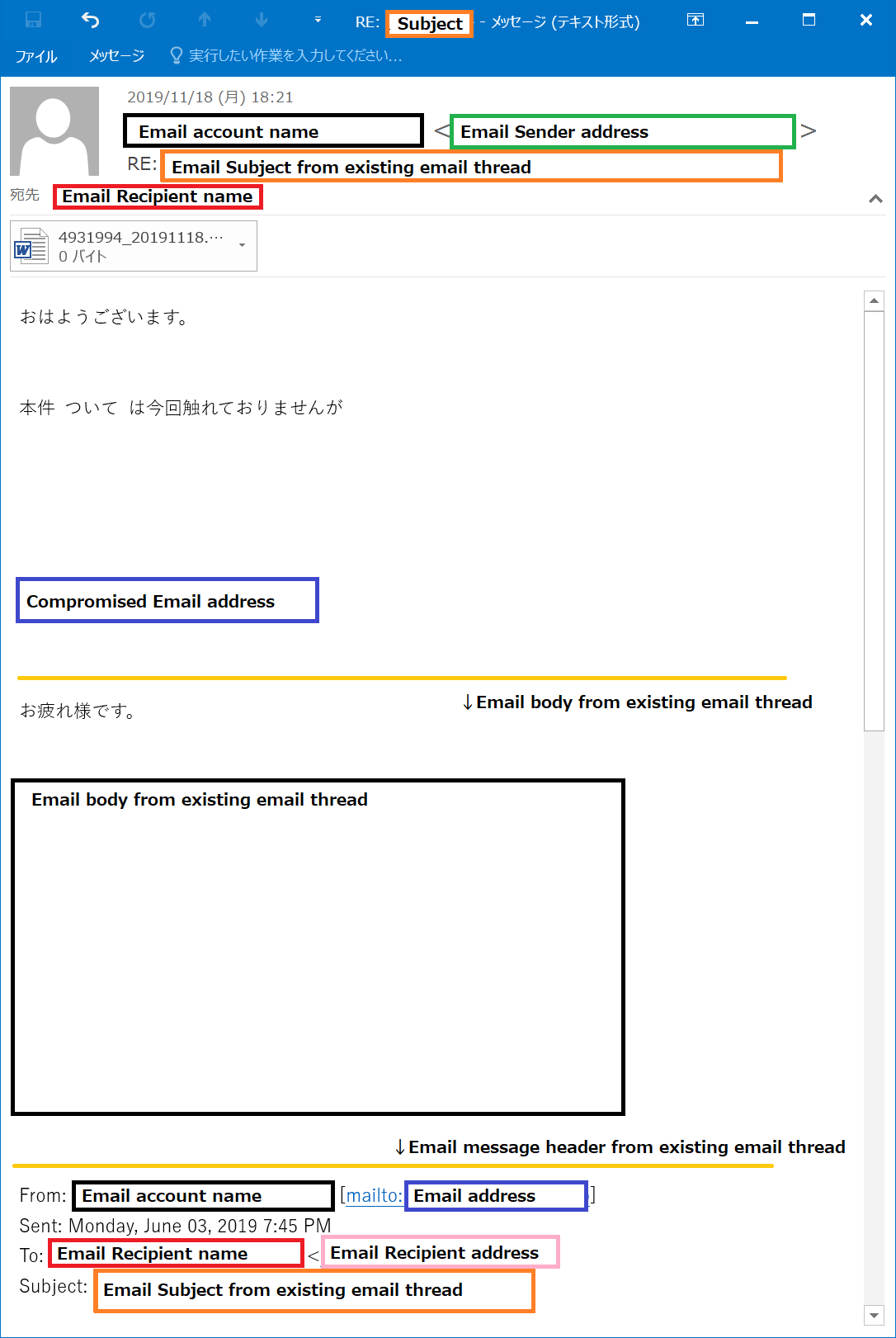
[Image 1: Email Example]
Some emails attached with a Word format file that lead to Emotet infection are created based on information stolen by Emotet. There are other cases that the message body contains the emails exchanged in the past and appears to be a reply to existing email thread.Therefore, it is necessary to be careful of these emails as they may have been sent from the attacker side using the information stolen by Emotet, although they appear to be sent from existing business partner personnel.
The attached file contains information that prompts you to enable the content, and Emotet will be downloaded once it is enabled.Depending on the Microsoft Word settings, Emotet may be downloaded without the warning.
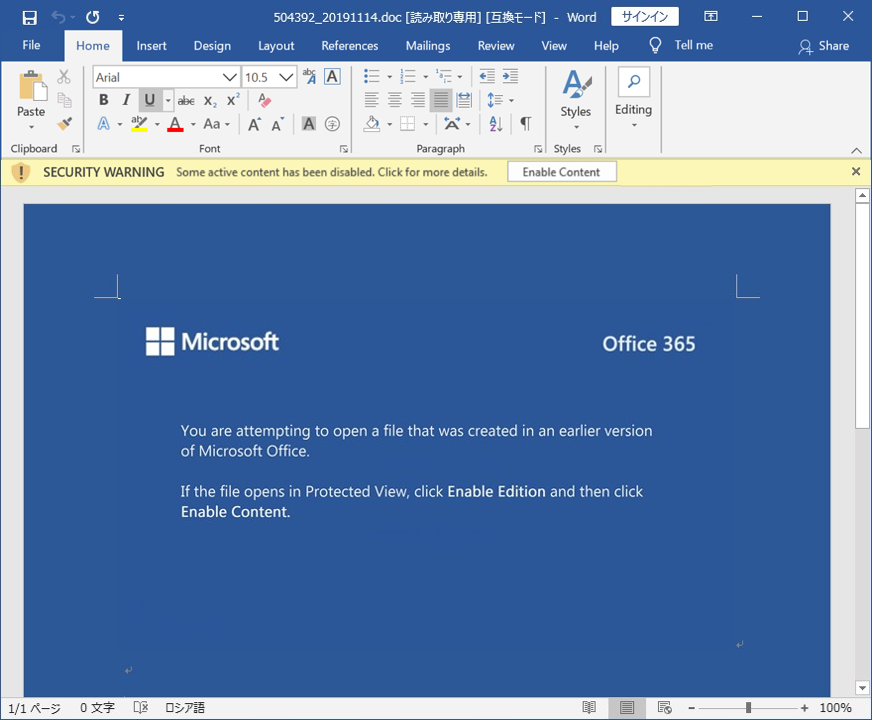
[Image 2: Attachment File Example]
- Authentication information such as passwords stored on the device or browser may be stolen
- Emotet infection may spread within the network by leveraging SMB exploits by using the stolen passwords
- Email account and its password may be stolen
- Email text and address book information may be stolen
- Stolen email account and body texts may be exploited to send malicious emails
Upon Emotet infection, information is stolen from the infected device, and then emails that spread the infection to customers and business partners might be delivered from the attackers'infrastructure. In addition, if the infected device remains in the organization, it could be exploited by attackers as a bot and send a large amount of suspicious emails to external network.
- Raise awareness in your organization through alert and advisory
- Disable automatic execution of Word macro *
- Detection of emails attached with malware by introducing email security products
- Enable email audit log
- Regularly apply OS patches (measures against spreading infection with SMB vulnerabilities)
- Obtain periodic offline backup (measures against targeted ransomware attacks)
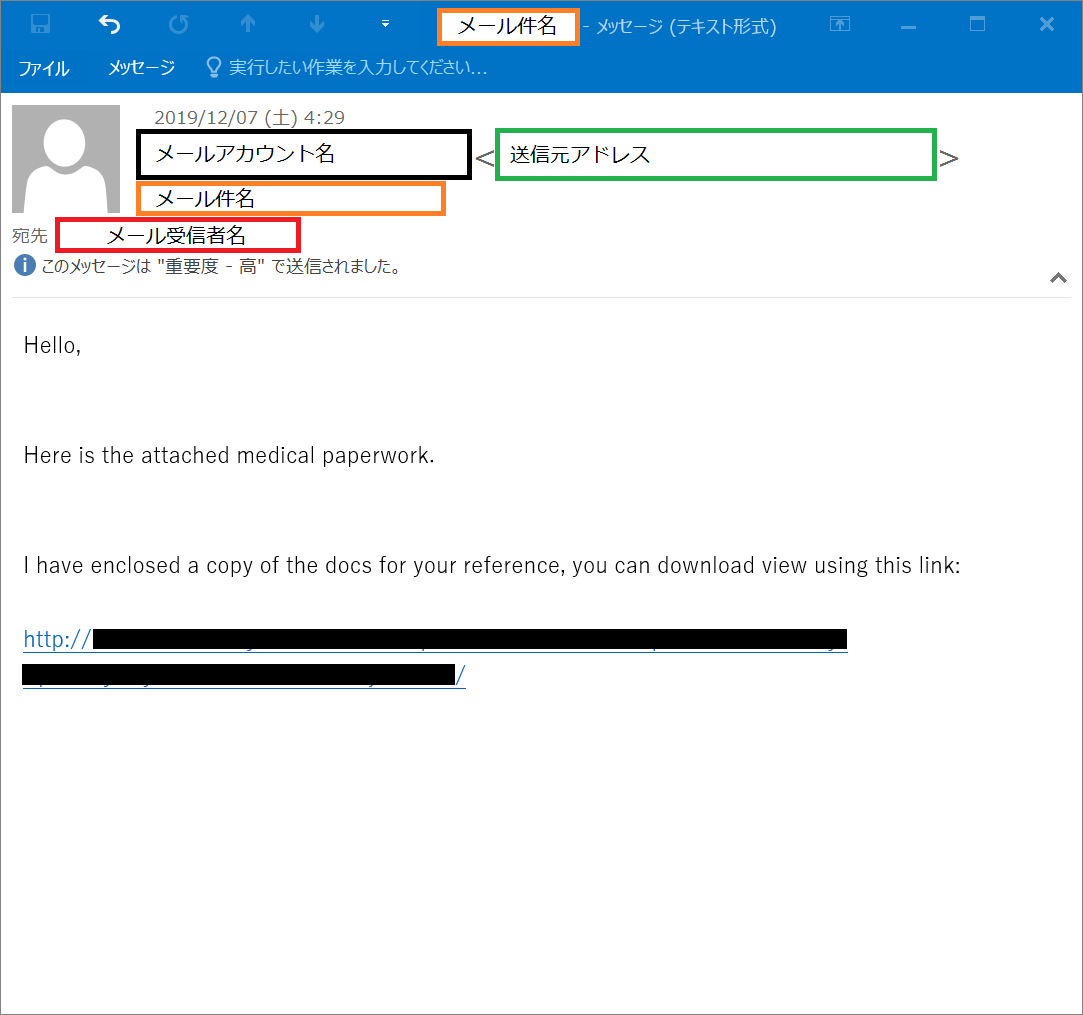
* Select "Disable all macros with notification" in the Microsoft Office Trust Center Macro Settings.
[image 3: Microsoft Office Trust Center Macro Settings]
- You are informed by an external organization that they received an email that appears to be coming from your organization's email address with an attached Word format file
- You check your organization's mail server, etc. and confirm that a large number of emails with Word format attachment or spoofed emails have been sent
If Emotet infection is confirmed in a device or system of your organization, it is recommended to take the following actions as an initial response in order to prevent further impact.
- Isolate the infected device from the network
- Change the password of the email account used in the infected device
Then, the following investigations and actions should be considered after consulting with a security vendor as necessary.
- Scan all devices in the organization with anti-virus software
- Change the password of accounts that are used in the infected device
- Monitor network traffic logs
- Initialize the infected device after investigation
US-CERT
Alert (TA18-201A) Emotet Malware
https://www.us-cert.gov/ncas/alerts/TA18-201A
Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC)
Advisory 2019-131a: Emotet malware campaign
https://www.cyber.gov.au/threats/advisory-2019-131a-emotet-malware-campaign
If you have any information regarding this alert, please contact JPCERT/CC.
2019-12-02 Updated "I. Overview"
2019-12-06 Updated TEL number at the bottom
2019-12-10 Updated "II. Attack Vector"
JPCERT Coordination Center (JPCERT/CC)
MAIL: ew-info@jpcert.or.jp
TEL: +81-3-6811-0610 FAX: +81-3-6271-8908
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/english/
JPCERT/CC
2019-11-27(Initial)
2019-12-10(Update)
I. Overview
Since the second half of October 2019, JPCERT/CC has been receiving reports regarding Emotet malware infection. Many of the reports were from victims who had received emails with a malicious Word format file attachment, impersonating a legitimate organization or person.Following this situation, in order to prevent further impact caused by Emotet malware, JPCERT/CC decided to publish this alert to share the primary infection vector of Emotet and its impact, as well as some tips on how to detect and defend against Emotet infection, and how to respond once the infection is confirmed.
Update: December 2, 2019 Update
JPCERT/CC published a blog on JPCERT/CC Eyes that summerized the FAQ for Emotet malware. Please also refer to this blog for more information.
JPCERT/CC Eyes
FAQ for Emotet malware handling
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/ja/2019/12/emotetfaq.html
JPCERT/CC Eyes
FAQ for Emotet malware handling
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/ja/2019/12/emotetfaq.html
II. Attack Vector
Cases of Emotet infection that JPCERT/CC is aware of are mostly triggered by executing a malicious Word format file and then"enabling content" of the document. Following is an example image of emails which may lead to Emotet malware infection.[Image 1: Email Example]
Some emails attached with a Word format file that lead to Emotet infection are created based on information stolen by Emotet. There are other cases that the message body contains the emails exchanged in the past and appears to be a reply to existing email thread.Therefore, it is necessary to be careful of these emails as they may have been sent from the attacker side using the information stolen by Emotet, although they appear to be sent from existing business partner personnel.
The attached file contains information that prompts you to enable the content, and Emotet will be downloaded once it is enabled.Depending on the Microsoft Word settings, Emotet may be downloaded without the warning.
[Image 2: Attachment File Example]
Update: December 10, 2019 Update
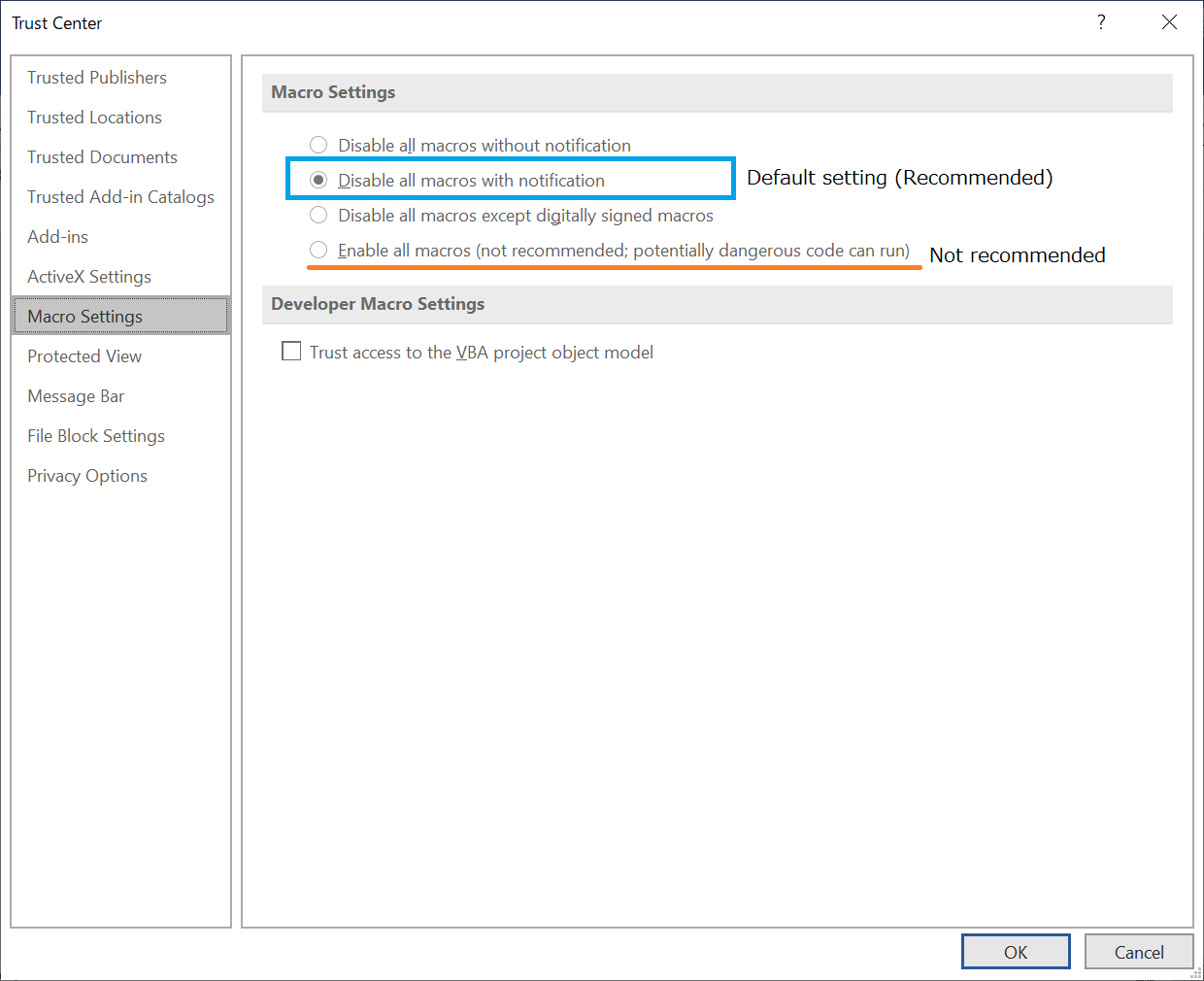
Since around December 6, 2019, JPCERT/CC has observed emails with URL link in the body of the message, which lead to Emotet infection.Once a recipient clicks the URL link in the email body, a Word format file is downloaded. Then Emotet is downloaded if the recipient enables the content after opening the file.
[Image 4: Email Example]
It is recommended to stay alerted for emails with URL link in the message body such as above, and not to click the URL link. Attack vectors of Emotet have been changed and may change in the future.Therefore, regardless of previous Emotet attack vectors, we would recommend not to execute an attachment file or click URL links on suspicious emails. Also, it is important to keep the emergency point of contact and reporting structure in your organization up-to-date.
[Image 4: Email Example]
It is recommended to stay alerted for emails with URL link in the message body such as above, and not to click the URL link. Attack vectors of Emotet have been changed and may change in the future.Therefore, regardless of previous Emotet attack vectors, we would recommend not to execute an attachment file or click URL links on suspicious emails. Also, it is important to keep the emergency point of contact and reporting structure in your organization up-to-date.
III. Impact
When infected with Emotet, the following events may occur.- Authentication information such as passwords stored on the device or browser may be stolen
- Emotet infection may spread within the network by leveraging SMB exploits by using the stolen passwords
- Email account and its password may be stolen
- Email text and address book information may be stolen
- Stolen email account and body texts may be exploited to send malicious emails
Upon Emotet infection, information is stolen from the infected device, and then emails that spread the infection to customers and business partners might be delivered from the attackers'infrastructure. In addition, if the infected device remains in the organization, it could be exploited by attackers as a bot and send a large amount of suspicious emails to external network.
IV. Countermeasures
Please consider the following actions to prevent Emotet infection and minimize damage caused by the infection.- Raise awareness in your organization through alert and advisory
- Disable automatic execution of Word macro *
- Detection of emails attached with malware by introducing email security products
- Enable email audit log
- Regularly apply OS patches (measures against spreading infection with SMB vulnerabilities)
- Obtain periodic offline backup (measures against targeted ransomware attacks)
* Select "Disable all macros with notification" in the Microsoft Office Trust Center Macro Settings.
[image 3: Microsoft Office Trust Center Macro Settings]
V. Post infection
In addition to the case where anti-virus software used in your organization detects and discovers the Emotet infection, if either of the following situations is confirmed, one or more devices in the organization may be infected with Emotet.- You are informed by an external organization that they received an email that appears to be coming from your organization's email address with an attached Word format file
- You check your organization's mail server, etc. and confirm that a large number of emails with Word format attachment or spoofed emails have been sent
If Emotet infection is confirmed in a device or system of your organization, it is recommended to take the following actions as an initial response in order to prevent further impact.
- Isolate the infected device from the network
- Change the password of the email account used in the infected device
Then, the following investigations and actions should be considered after consulting with a security vendor as necessary.
- Scan all devices in the organization with anti-virus software
- Change the password of accounts that are used in the infected device
- Monitor network traffic logs
- Initialize the infected device after investigation
VI. References
US-CERT
Alert (TA18-201A) Emotet Malware
https://www.us-cert.gov/ncas/alerts/TA18-201A
Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC)
Advisory 2019-131a: Emotet malware campaign
https://www.cyber.gov.au/threats/advisory-2019-131a-emotet-malware-campaign
If you have any information regarding this alert, please contact JPCERT/CC.
Update: December 6, 2019 Update
We corrected the TEL number below as it was incorrect. We apologize for any inconvenience caused.
Revision History
2019-11-27 First edition2019-12-02 Updated "I. Overview"
2019-12-06 Updated TEL number at the bottom
2019-12-10 Updated "II. Attack Vector"
JPCERT Coordination Center (JPCERT/CC)
MAIL: ew-info@jpcert.or.jp
TEL: +81-3-6811-0610 FAX: +81-3-6271-8908
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/english/